Large Language Models
The following post was generated by ChatGPT when I asked it to generate a couple of praragraphs about LLMs when this was posted. I wanted to keep this post just as a reference so that we can look back and laugh at how naive we were.
LLMs
Large language models represent a groundbreaking achievement in artificial intelligence, leveraging deep learning techniques to process and generate human-like text at an unprecedented scale. These models have a rich history and are continually evolving, offering immense potential for various applications while also raising important ethical and societal considerations.
The history of large language models can be traced back to the development of neural networks and natural language processing (NLP) in the 20th century. Early efforts, such as rule-based systems and statistical language models, laid the groundwork for understanding language, but it was the advent of deep learning and the introduction of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that marked a significant turning point. These architectures enabled models to process sequential data like text more effectively, but they were limited by their inability to capture long-range dependencies in language.
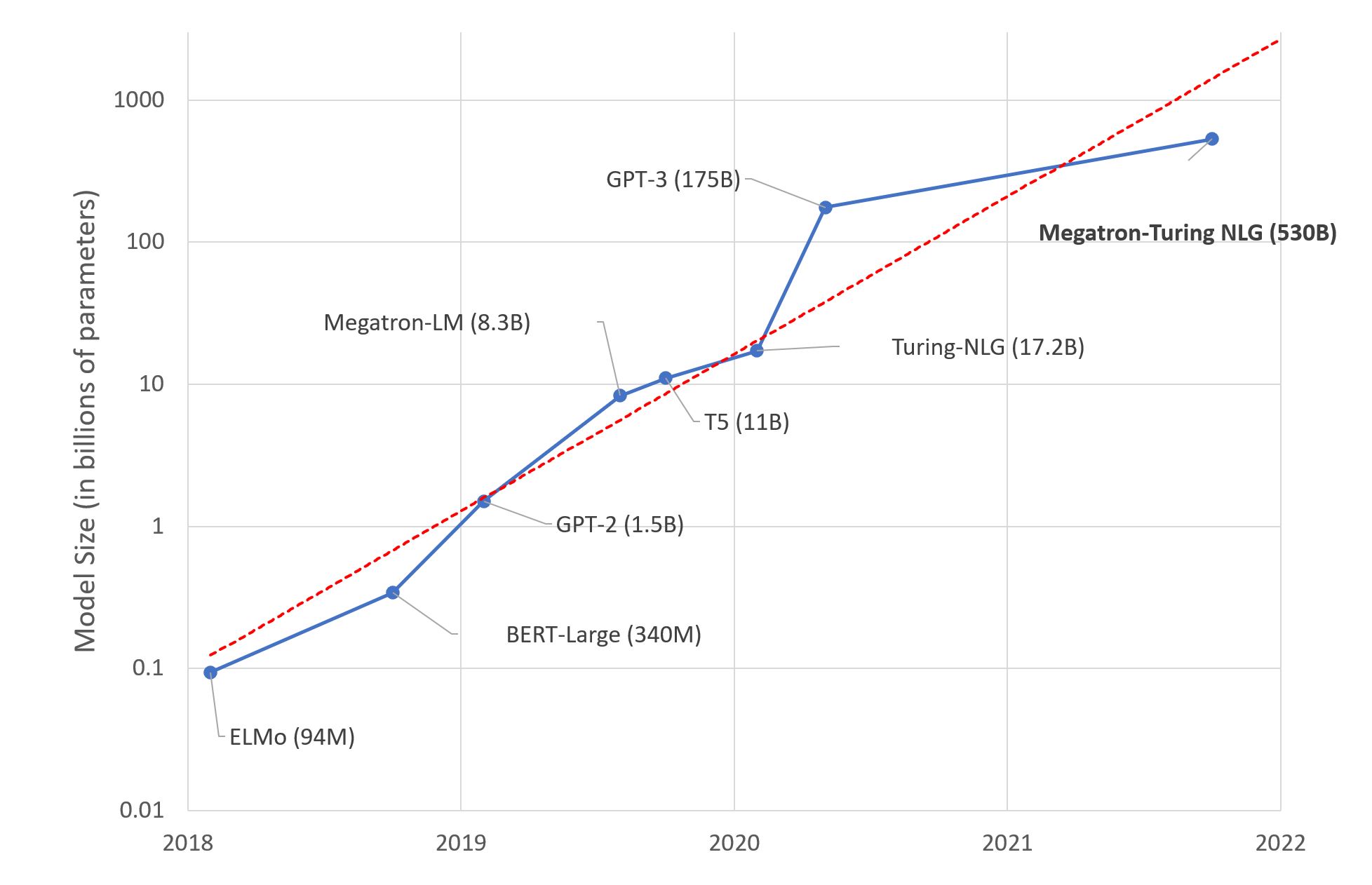
The breakthrough came with the introduction of transformer architecture in the form of models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers). These models, particularly GPT-3, with its 175 billion parameters, demonstrated an extraordinary capacity to understand and generate text. They were pre-trained on vast amounts of text data from the internet and could be fine-tuned for various NLP tasks, from language translation to sentiment analysis, chatbots, and more. This pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm made large language models versatile and widely applicable.
Large language models were already being integrated into various industries, including healthcare, finance, customer support, and content generation. They were also used for research in fields like climate science, drug discovery, and social sciences. However, ethical concerns about bias, misinformation, and the environmental impact of training such large models were hotly debated.
Looking to the future, the capabilities of large language models are expected to continue expanding. This evolution will likely involve models with even larger parameter sizes, improved fine-tuning techniques, and enhanced understanding of context and user intent. Advancements in hardware, like specialized AI chips and more energy-efficient training methods, will also contribute to their development. Additionally, research into addressing bias, improving explainability, and ensuring the responsible deployment of these models will be essential.
In summary, large language models have come a long way in a relatively short time, transforming the landscape of AI and NLP. Their history is marked by a progression from traditional NLP methods to the transformer architecture, and their current state is characterized by widespread adoption and exploration of their capabilities across various domains. In the future, we can anticipate even more powerful and responsible applications of large language models as they continue to push the boundaries of AI and our understanding of language processing.